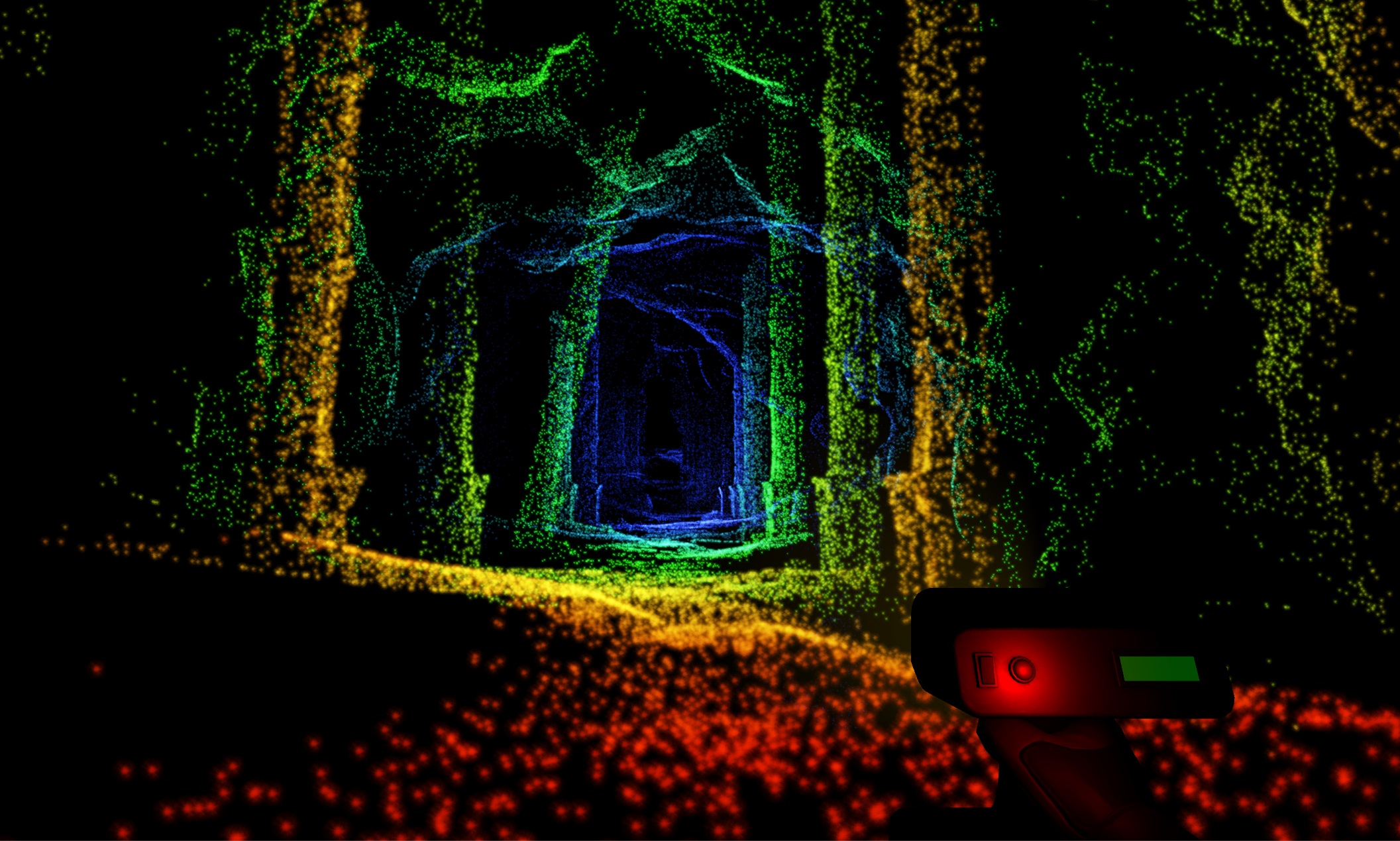
Introduction
In the realm of cutting-edge technology, Lidar scanners have emerged as a revolutionary tool, transforming the way we perceive and interact with the world. Short for https://www.ctnewswire.com/ Light Detection and Ranging, Lidar employs laser beams to measure distances and create detailed, three-dimensional maps of the environment. In this article, we explore the multifaceted capabilities of Lidar scanners, their applications across industries, and the profound impact they have on various fields.
Unveiling the Technology Behind Lidar Scanners
At its core, a Lidar scanner operates emitting laser beams and measuring the time it takes for the light to return after hitting an object. This data is then processed to create highly accurate and detailed maps of the surroundings. Lidar scanners are equipped with advanced sensors, allowing them to capture not only the distance to objects but also their shapes and contours.
Applications Across Industries
1. Autonomous Vehicles
One of the most prominent applications of Lidar technology is in autonomous vehicles. Lidar scanners play a pivotal role in providing real-time, high-resolution mapping of the vehicle’s surroundings. This enables autonomous cars to navigate safely detecting obstacles, pedestrians, and other vehicles, contributing to the advancement of self-driving technology.
2. Surveying and Mapping
Lidar scanners have revolutionized the field of surveying and mapping. Traditional methods often fall short in capturing detailed topographical information, especially in challenging terrains. Lidar technology allows surveyors to create precise and comprehensive maps for urban planning, environmental monitoring, and geological surveys.
3. Environmental Monitoring
In environmental science, Lidar scanners are employed for vegetation analysis, forest mapping, and monitoring changes in landscapes. The ability to capture detailed 3D data facilitates accurate assessments of biodiversity, deforestation, and ecological shifts, aiding conservation efforts and sustainable resource management.
4. Construction and Architecture
Architects and construction professionals leverage Lidar scanners for site analysis and building information modeling (BIM). The technology provides detailed scans of existing structures and landscapes, facilitating the planning and design processes. Lidar’s accuracy is invaluable in ensuring precision in construction projects.
5. Archeological Discoveries
Lidar scanners have played a crucial role in archeology uncovering hidden landscapes and archaeological sites. The technology can penetrate dense vegetation and terrain, revealing ancient structures and artifacts that might otherwise remain undiscovered. This has led to significant advancements in our understanding of historical civilizations.
Advancements in Lidar Technology
As technology continues to evolve, Lidar scanners are becoming more compact, affordable, and versatile. Miniaturized Lidar sensors are now integrated into various devices, including smartphones and drones, expanding the accessibility of this technology across different domains.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its numerous advantages, Lidar technology faces challenges such as cost, size, and the need for improved standardization. Ongoing research and development aim to address these issues, with the goal of making Lidar more accessible to a broader range of industries.
Conclusion
Lidar scanners stand at the forefront of technological innovation, reshaping industries and unlocking new possibilities. From revolutionizing transportation with autonomous vehicles to unveiling hidden aspects of our environment, Lidar technology continues to leave an indelible mark on the way we perceive and interact with the world. As advancements persist, the applications of Lidar scanners are poised to expand, ushering in an era of unprecedented precision and insight.