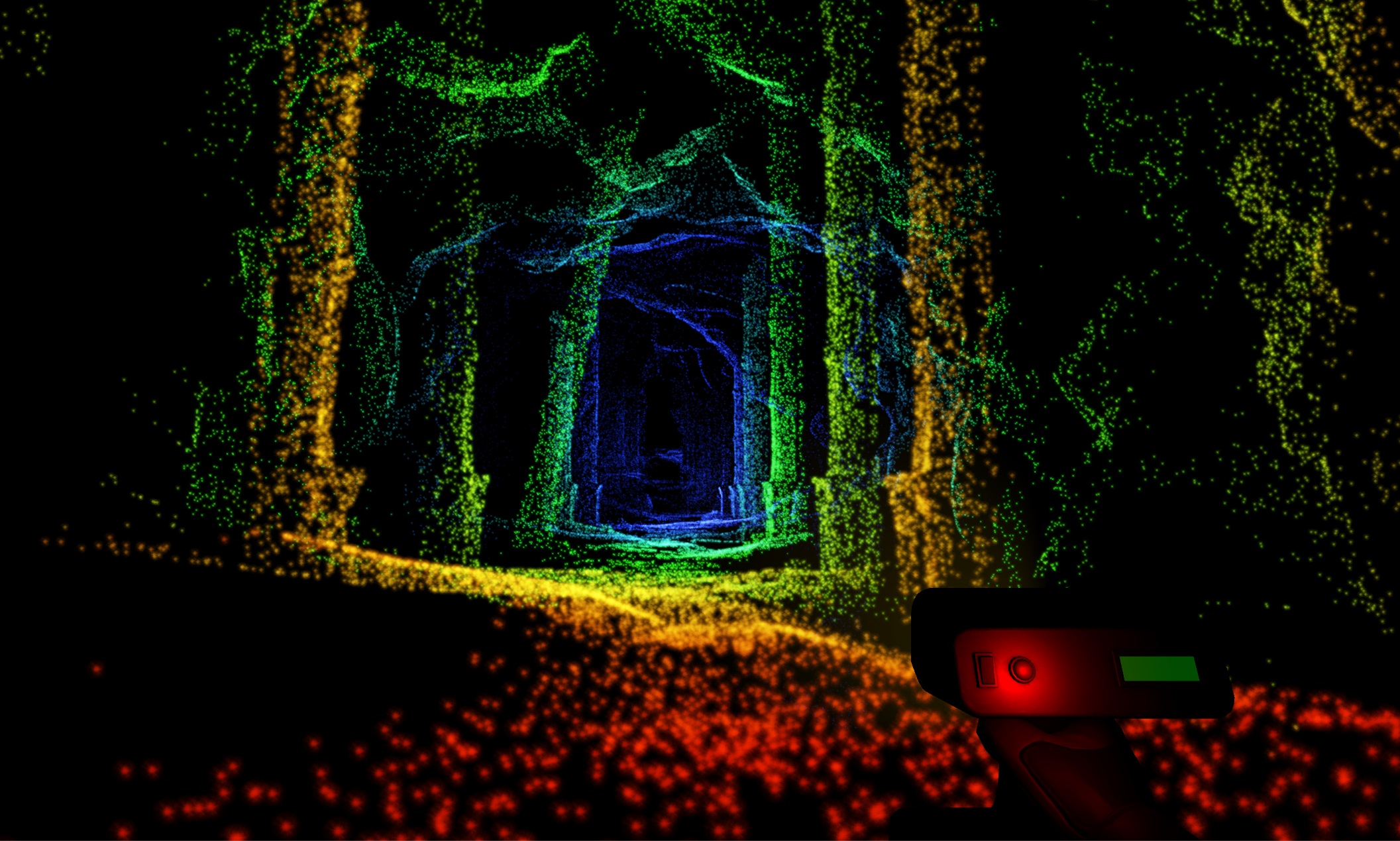
Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) is a rapidly evolving technology with the potential to revolutionize various fields. From self-driving cars to surveying landscapes and creating virtual reality experiences, lidar is proving its versatility and power.
How Does Lidar Work?
Lidar systems work by transmitting laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for the reflected light to return. By analyzing the time of flight, the system can accurately calculate the distance to the reflecting surface. This process is repeated millions of times per second, generating a dense point cloud that represents the surrounding environment in 3D.
Applications of Lidar Technology
- Autonomous Vehicles: Lidar sensors play a crucial role in self-driving cars, enabling them to accurately perceive their surroundings and navigate mttimes.us safely. By creating a 3D map of their environment, lidar helps autonomous vehicles detect and avoid obstacles, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
- 3D Mapping and Surveying: Lidar is extensively used for creating precise 3D maps of large areas, including cities, forests, and construction sites. This data is valuable for infrastructure planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster relief efforts.
- Precision Agriculture: Lidar technology is used in precision agriculture to monitor crop health, estimate yield, and optimize irrigation and fertilization. By providing insights into plant growth and canopy structure, lidar helps farmers increase efficiency and sustainability.
- Archaeological Research: Lidar has revolutionized archaeological research by allowing archaeologists to map hidden structures and uncover buried cities beneath dense vegetation. This technology has led to significant discoveries and expanded our understanding of ancient civilizations.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: Lidar is increasingly used in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications to create realistic and immersive experiences. By accurately capturing the dimensions and details of real-world environments, lidar helps developers create virtual worlds that feel more natural and engaging.
Benefits of Using Lidar
- High Accuracy: Lidar provides highly accurate distance measurements, making it ideal for applications requiring precise 3D data.
- Long Range: Lidar sensors can operate over long distances, enabling them to map large areas efficiently.
- All-Weather Performance: Lidar technology works day or night and in various weather conditions, making it a reliable tool for outdoor applications.
- Rich Data: Lidar generates rich data sets that can be analyzed to extract valuable information about the environment.
Challenges and Future of Lidar
While lidar offers significant benefits, there are also some challenges associated with its adoption. These include:
- Cost: Lidar systems can be expensive, making them less accessible to some users.
- Data Processing: Processing large lidar datasets requires substantial computational resources.
- Regulations: The use of lidar technology may be subject to regulations, depending on the application and location.
Despite these challenges, the future of lidar is promising. As technology advances and costs decrease, we can expect to see lidar becoming even more widespread in various industries and applications. With its unique capabilities, lidar is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of technology and innovation.